INTRODUCTION
Automobile Industry
The Indian automobile industry is a vital economic indicator, with
the two-wheeler segment dominating due to a growing middle class
and youth population. Rural market exploration by companies has
further boosted growth. Commercial vehicles are in demand due to
logistics and passenger transportation industries. The future is
promising, with the electrification of three-wheelers and small
passenger vehicles expected to drive growth. India holds a strong
position globally in heavy vehicles, being a top tractor, bus, and
heavy truck producer.
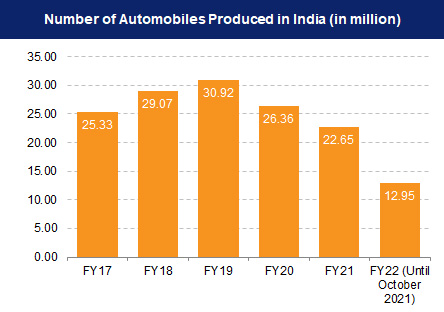
In FY22, India produced 22.93 million
vehicles, with robust domestic demand and exports. In FY23,
passenger vehicle sales reached 3.89 million, and exports totaled
4,761,487. This sector's contribution to the national GDP has
risen from 2.77% in 1992-1993 to around 7.1% today, employing
approximately 19 million people directly and indirectly. India is
a notable auto exporter, with government initiatives like the
Automotive Mission Plan 2026, scrappage policy, and
production-linked incentive scheme aiming to establish India as a
global leader in the two-wheeler and four-wheeler market by 2022.

MARKET SIZE
1. Passenger Car Market: In 2021, the Indian passenger car market was valued at approximately US$ 32.70 billion. It's projected to grow significantly, reaching an estimated value of US$ 54.84 billion by 2027, with a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of over 9% between 2022 and 2027. This growth is indicative of the expanding market for passenger cars in India.
2. Global EV Market: The global electric vehicle (EV) market was worth around US$ 250 billion in 2021. By 2028, it's expected to grow nearly fivefold, reaching approximately US$ 1,318 billion. This reflects the substantial and accelerating worldwide interest in electric vehicles as an eco-friendly alternative to traditional gasoline-powered cars.
3. Indian EV Market: The electric vehicle market in India is also experiencing rapid growth. It is projected to be worth around Rs. 50,000 crore (US$ 7.09 billion) by 2025. A study by the Council on Energy, Environment and Water (CEEW) and the Centre for Energy Finance (CEF) has identified a significant opportunity of US$ 206 billion for electric vehicles in India by 2030. Realizing this opportunity would require a substantial investment of US$ 180 billion in vehicle manufacturing and charging infrastructure.
4. EV Finance Industry: According to NITI Aayog and the Rocky Mountain Institute (RMI), India's EV finance industry is expected to reach Rs. 3.7 lakh crore (US$ 50 billion) by 2030. This underlines the growing financial support and investment in the electric vehicle sector in India.
5. EV Market Growth and Battery Market: The EV market in India is anticipated to expand at a CAGR of 36% until 2026, according to the India Energy Storage Alliance. Additionally, the EV battery market is expected to grow at a CAGR of 30% during the same period. This highlights the increasing focus on electric vehicles and related battery technology.
6. Automobile Exports: The Indian automotive industry has set ambitious targets to increase vehicle exports. It aims to achieve a fivefold increase in exports from 2016 to 2026. In FY23, India exported a total of 47,61,487 vehicles, with two-wheelers accounting for a significant portion at 36,52,122 units. This underscores India's role as a notable player in the global automobile export market.
The Indian automobile industry is a vital economic indicator, with the two-wheeler segment dominating due to a growing middle class.Indian automotive industry is targeting to increase the export of vehicles by five times during 2016-26. In FY23, total automobile exports from India stood at 47,61,487. Indian automobile exports of two-wheelers stood at 36,52,122 in FY23. The Indian automobile industry is experiencing robust growth, with a strong focus on electric vehicles, both in terms of manufacturing and infrastructure development. The industry is also looking to significantly increase its presence in the global automobile export market.These developments are indicative of India's evolving position in the automotive and electric vehicle sectors
ROAD AHEAD
Turning Ideas into Reality
In August 2022, the Indian government launched India’s first double-decker electric bus in Mumbai. Looking long term, the government feels it is necessary to overhaul the country’s transportation system. It is working to create an integrated electric vehicle (EV) mobility ecosystem with a low carbon footprint and high passenger density with an emphasis on urban transportation reform. The government's strategy and policies are intended to promote greater adoption of electric vehicles in response to growing customer demand for cleaner transportation options. The Government of India expects the automobile sector to attract US$ 8-10 billion in local and foreign investments by 2023. India could be a leader in shared mobility by 2030, providing opportunities for electric and autonomous vehicles.

Quick Links
© Jaikvik Business India Private Limited. All Rights Reserved.
